Nvidia announces Arm-based Grace CPU "Superchip"
The 144-core processor is destined for AI infrastructure and high performance computing


Nvidia has released new chips, servers, and a supercomputer to bolster the AI and high-performance computing (HPC) capabilities of its offerings.
The company unveiled the new technologies - which includes a new data centre "Superchip" 0 at a conference this week, where the new silicon and data centre scale systems were introduced to the public.
What is the Nvidia Grace CPU Superchip?
The company announced the Nvidia Grace CPU "Superchip", consisting of two CPU chips connected over NVLink-C2C, a new high-speed, low-latency, chip-to-chip interconnect.
This data centre CPU has been designed for AI infrastructure and HPC, providing the highest performance and twice the memory bandwidth and energy efficiency compared to today’s leading server chips, stated the company.
It packs 144 Arm cores in a single socket and has a memory subsystem of LPDDR5x memory with Error Correction Code for the best balance of speed and power consumption. The memory subsystem offers double the bandwidth of traditional DDR5 designs at 1 terabyte a second while consuming less power as the CPU consumes 500 watts.
“A new type of data centre has emerged — AI factories that process and refine mountains of data to produce intelligence,” said Jensen Huang, founder and CEO of Nvidia. “The Grace CPU Superchip offers the highest performance, memory bandwidth and NVIDIA software platforms in one chip and will shine as the CPU of the world’s AI infrastructure.”
The Grace Superchip is based on the latest data centre architecture, Arm v9, and will run all of Nvidia’s computing software stacks. Nvidia said it will excel at the most demanding HPC, AI, data analytics, scientific computing, and hyperscale computing applications. It is expected to be available in the first half of 2023.
Get the ITPro daily newsletter
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
What is the NVIDIA H100 GPU?
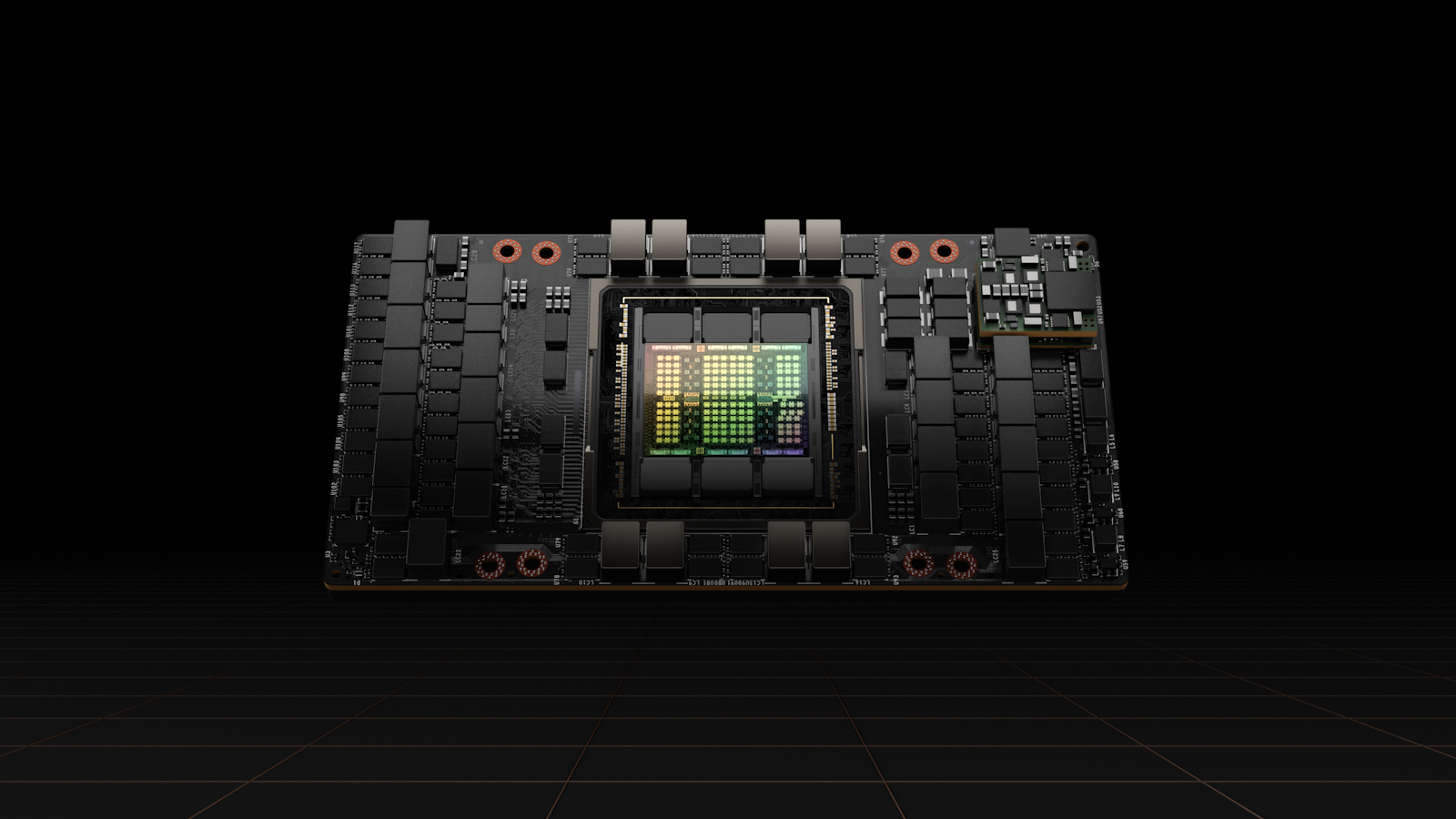

The company has also announced its first Hopper-based GPU, the Nvidia H100, which the company claims is the world’s largest and most powerful accelerator. The Hopper architecture is Nvidia’s new next-generation accelerated computing platform, replacing the Nvidia Ampere architecture launched two years ago.
Nvidia said that the H100 features major advances to accelerate AI, HPC, memory bandwidth, interconnect, and communication, including 5 terabytes per second of external connectivity. It’s the first GPU to support PCIe Gen5 and the first to use HBM3, enabling 3 TB/s of memory bandwidth.
The company underlined that twenty H100 GPUs can sustain the equivalent of the entire world’s internet traffic, making it possible for its customers to deliver advanced recommender systems and large language models running inference on data in real-time.
It also has second-generation secure multi-instance GPU (MIG), meaning a single GPU can be partitioned into seven smaller, fully isolated instances, to handle different types of jobs. The Hopper architecture extends MIG capabilities by up to 7x over the previous generation by offering secure multi-tenant configurations in cloud environments across each GPU instance.
"Data centres are becoming AI factories -- processing and refining mountains of data to produce intelligence," said Huang. "NVIDIA H100 is the engine of the world's AI infrastructure that enterprises use to accelerate their AI-driven businesses."
Nvidia added that H100 is the world’s first accelerator with confidential computing capabilities to protect AI models and customer data while they are being processed. Its customers will be able to apply confidential computing to federated learning for privacy-sensitive industries like healthcare and financial services, as well as on shared cloud infrastructures.
The Nvidia H100 will be available starting in the third quarter, added the company.
What is the Eos Supercomputer?
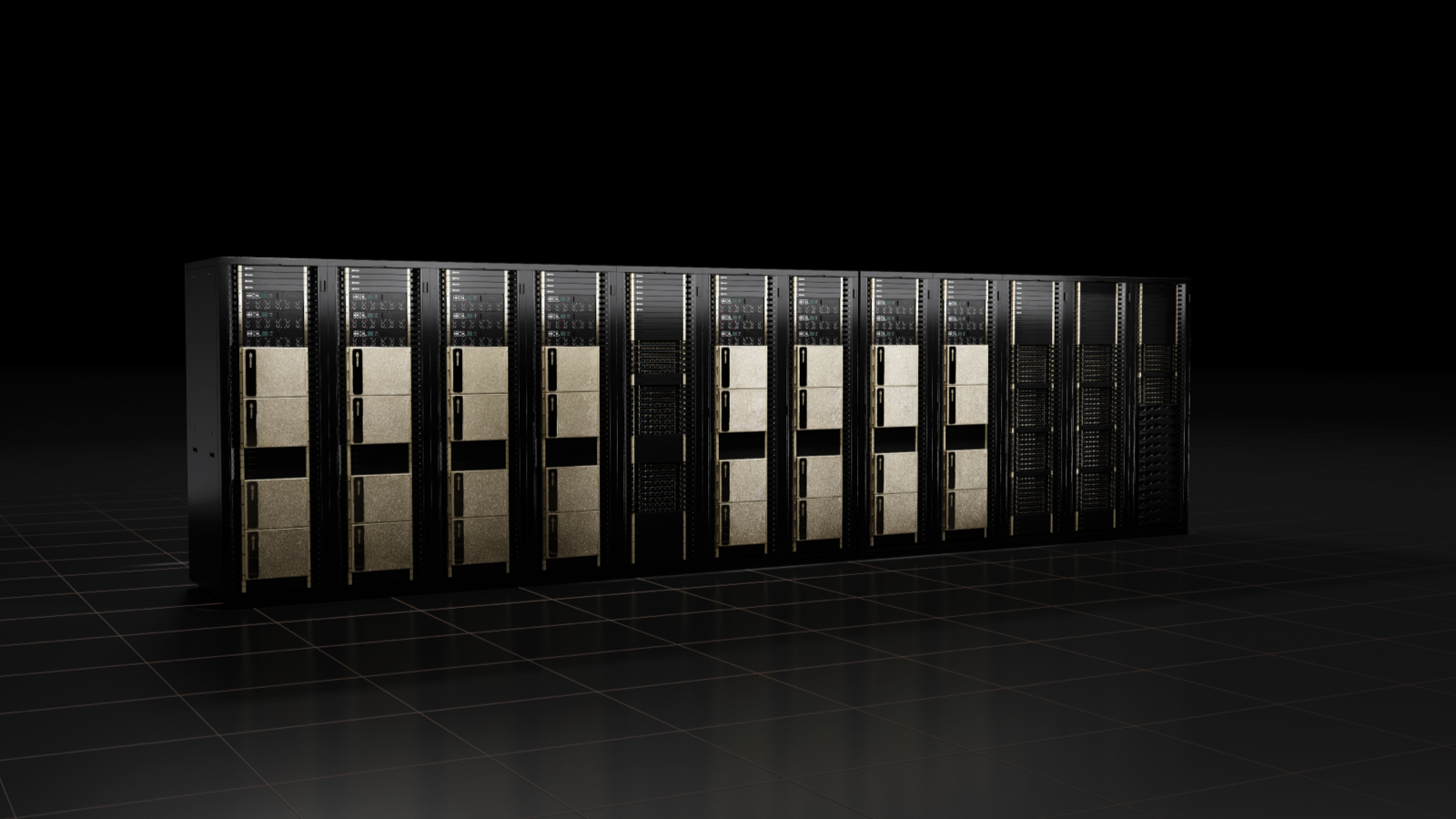

The chipmaker also announced its fourth-generation DGX system, which is its first AI platform to be built with the new H100 GPUs. Nvidia said that the system will deliver the scale demanded to meet the massive compute requirements of large language models, recommender systems, healthcare research, and climate science.
It highlighted that by packing eight H100 GPUs per system, each will provide 32 petaflops of AI performance, 6x more than the prior generation.
RELATED RESOURCE

Linked to this, Nvidia is also building the Nvidia Eos, which it says is expected to be the world’s fastest AI supercomputer after it begins operations later this year. It will feature a total of 576 DGX H100 systems with 4,608 H100 GPUs.
“AI has fundamentally changed what software can do and how it is produced. Companies revolutionising their industries with AI realise the importance of their AI infrastructure,” said Huang. “Our new DGX H100 systems will power enterprise AI factories to refine data into our most valuable resource — intelligence.”
It’s anticipated to provide 18.4 exaflops of AI computing performance, 4x faster AI processing than the Fugaku supercomputer in Japan, the world’s fastest system. Nvidia said that Eos will serve as a blueprint for advanced AI infrastructure from Nvidia, as well as its OEM and cloud partners.
Zach Marzouk is a former ITPro, CloudPro, and ChannelPro staff writer, covering topics like security, privacy, worker rights, and startups, primarily in the Asia Pacific and the US regions. Zach joined ITPro in 2017 where he was introduced to the world of B2B technology as a junior staff writer, before he returned to Argentina in 2018, working in communications and as a copywriter. In 2021, he made his way back to ITPro as a staff writer during the pandemic, before joining the world of freelance in 2022.
-
 Should AI PCs be part of your next hardware refresh?
Should AI PCs be part of your next hardware refresh?AI PCs are fast becoming a business staple and a surefire way to future-proof your business
By Bobby Hellard
-
 Westcon-Comstor and Vectra AI launch brace of new channel initiatives
Westcon-Comstor and Vectra AI launch brace of new channel initiativesNews Westcon-Comstor and Vectra AI have announced the launch of two new channel growth initiatives focused on the managed security service provider (MSSP) space and AWS Marketplace.
By Daniel Todd
-
 “The Grace Blackwell Superchip comes to millions of developers”: Nvidia's new 'Project Digits' mini PC is an AI developer's dream – but it'll set you back $3,000 a piece to get your hands on one
“The Grace Blackwell Superchip comes to millions of developers”: Nvidia's new 'Project Digits' mini PC is an AI developer's dream – but it'll set you back $3,000 a piece to get your hands on oneNews Nvidia unveiled the launch of a new mini PC, dubbed 'Project Digits', aimed specifically at AI developers during CES 2025.
By Solomon Klappholz
-
 Intel just won a 15-year legal battle against EU
Intel just won a 15-year legal battle against EUNews Ruled to have engaged in anti-competitive practices back in 2009, Intel has finally succeeded in overturning a record fine
By Emma Woollacott
-
 Jensen Huang just issued a big update on Nvidia's Blackwell chip flaws
Jensen Huang just issued a big update on Nvidia's Blackwell chip flawsNews Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang has confirmed that a design flaw that was impacting the expected yields from its Blackwell AI GPUs has been addressed.
By Solomon Klappholz
-
 How Nvidia took the world by storm
How Nvidia took the world by stormAnalysis Riding the AI wave has turned Nvidia into a technology industry behemoth
By Steve Ranger
-
 Meta unveils two new GPU clusters used to train its Llama 3 AI model — and it plans to acquire an extra 350,000 Nvidia H100 GPUs by the end of 2024 to meet development goals
Meta unveils two new GPU clusters used to train its Llama 3 AI model — and it plans to acquire an extra 350,000 Nvidia H100 GPUs by the end of 2024 to meet development goalsNews Meta is expanding its GPU infrastructure with the help of Nvidia in a bid to accelerate development of its Llama 3 large language model
By George Fitzmaurice
-
 TD Synnex buoyed by UK distribution deal with Nvidia
TD Synnex buoyed by UK distribution deal with NvidiaNews New distribution agreement covers the full range of Nvidia enterprise software and accelerated computing products
By Daniel Todd
-
 PCI consortium implies Nvidia at fault for its melting cables
PCI consortium implies Nvidia at fault for its melting cablesNews Nvidia said the issues were caused by user error but the PCI-SIG pointed to possible design flaws
By Rory Bathgate
-
 Nvidia warns rivals are exploiting uncertainty surrounding Arm’s future
Nvidia warns rivals are exploiting uncertainty surrounding Arm’s futureNews The company claims Intel and AMD have been getting ahead due to the drawn-out regulatory process
By Zach Marzouk