How to remote desktop into Ubuntu
Learn how to set up and use remote desktop access on Ubuntu, with easy-to-follow steps for both VNC and RDP solutions


Rene Millman
Ubuntu, one of the most widely used Linux distributions, is known for its user-friendly interface, vast software repository, and excellent hardware support. Whether you're running Ubuntu as your primary operating system or using it alongside Windows, the ability to remote desktop into Ubuntu can be essential for accessing files or troubleshooting remotely.
Fortunately, Ubuntu has built-in tools for remote desktop access, making it compatible with some of the best remote desktop software available, particularly the best remote desktop solutions for Linux. This guide will walk you through how to set up and use different methods for remote desktop access, including VNC, RDP, and third-party tools, allowing seamless access to your Ubuntu system from anywhere.
Remote Desktop Options for Ubuntu
Ubuntu includes a built-in remote desktop solution based on Virtual Network Computing (VNC), which allows you to connect remotely to your desktop without installing additional software. VNC is a popular cross-platform tool that works on all major operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and macOS, making it an accessible option for Ubuntu users..
To remote desktop into Ubuntu from another computer, you'll need a VNC client installed on the machine you're using to connect. Free clients like TightVNC for Windows or RealVNC’s Viewer for Android and iOS are excellent choices.
Alternatively, if you're more familiar with Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), Ubuntu supports this as well, but you'll need to install additional software like xRDP. We'll guide you through both methods, starting with VNC, the most commonly used approach.
For users who want to connect from their Ubuntu installation to other machines, the built-in Remmina client offers a versatile remote desktop solution, supporting a range of protocols like VNC, RDP, and SSH. This makes it easier to connect to other systems, including Windows and Linux, without requiring additional installations.
Step 1: How to Enable Screen Sharing on Ubuntu 24.04.1
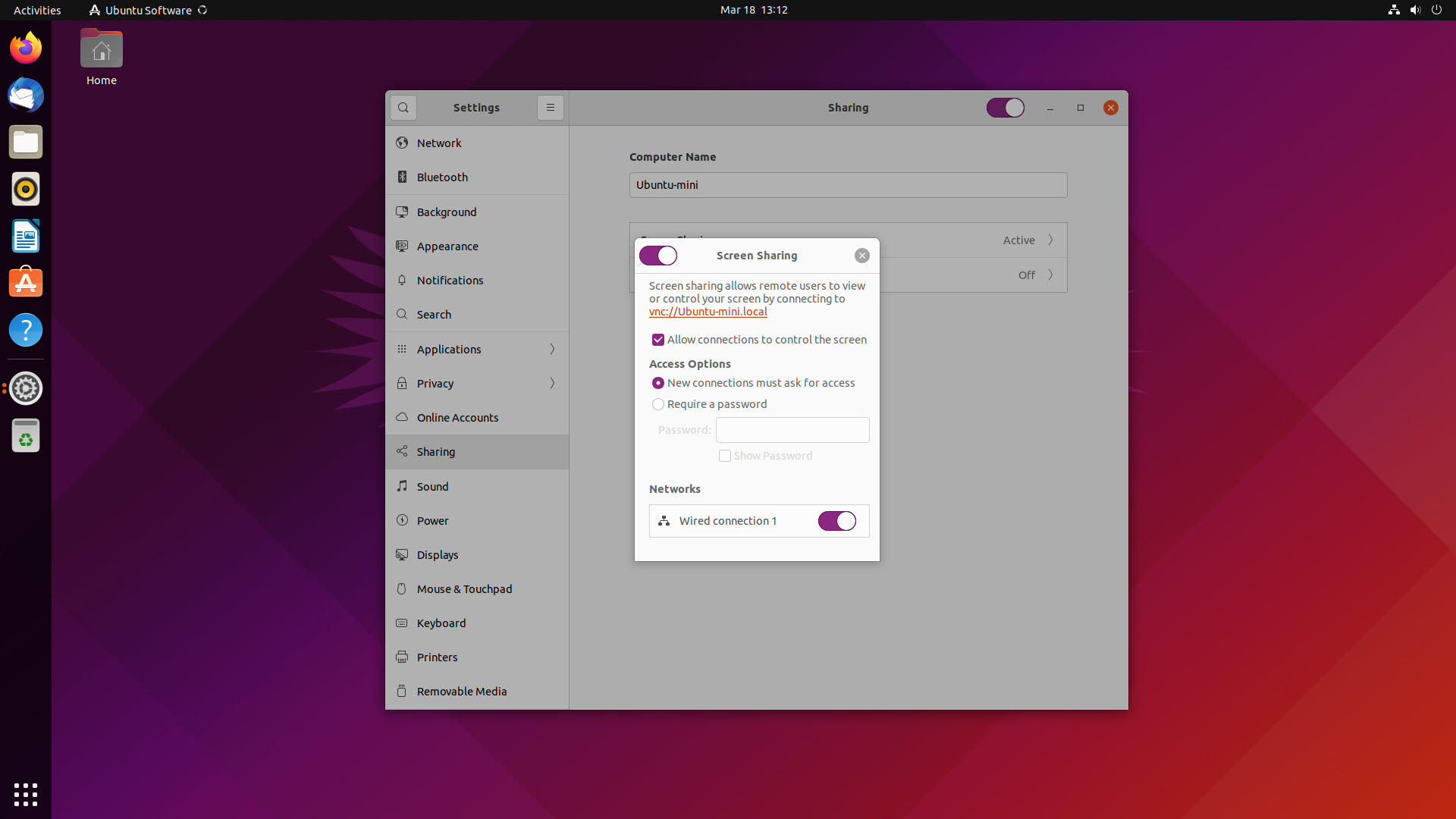
- Access system settings: Click on the Ubuntu symbol located in the bottom left corner of your desktop to open the main menu. From the menu, click on "System" to open the system settings.
- Open remote desktop settings: In the system settings window, select "Remote Desktop" from the list of options. This will take you to the screen-sharing settings.
- Enable desktop sharing: You will see two options at the top: "Desktop Sharing" and "Remote Control." To allow others to view your desktop, toggle the switch next to "Desktop Sharing" to turn it on.
- Enable remote control (optional): If you want others to control your desktop, toggle the switch next to "Remote Control" to enable remote access with control permissions.
- Connection information: Below these options, you’ll find important connection details such as your hostname, port number, and login credentials (username and password) that will be used by remote users to connect to your desktop.
After completing these steps, your Ubuntu machine will be ready to accept remote desktop connections via VNC.
Get the ITPro daily newsletter
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
Step 2: How to find the IP address of your Ubuntu computer
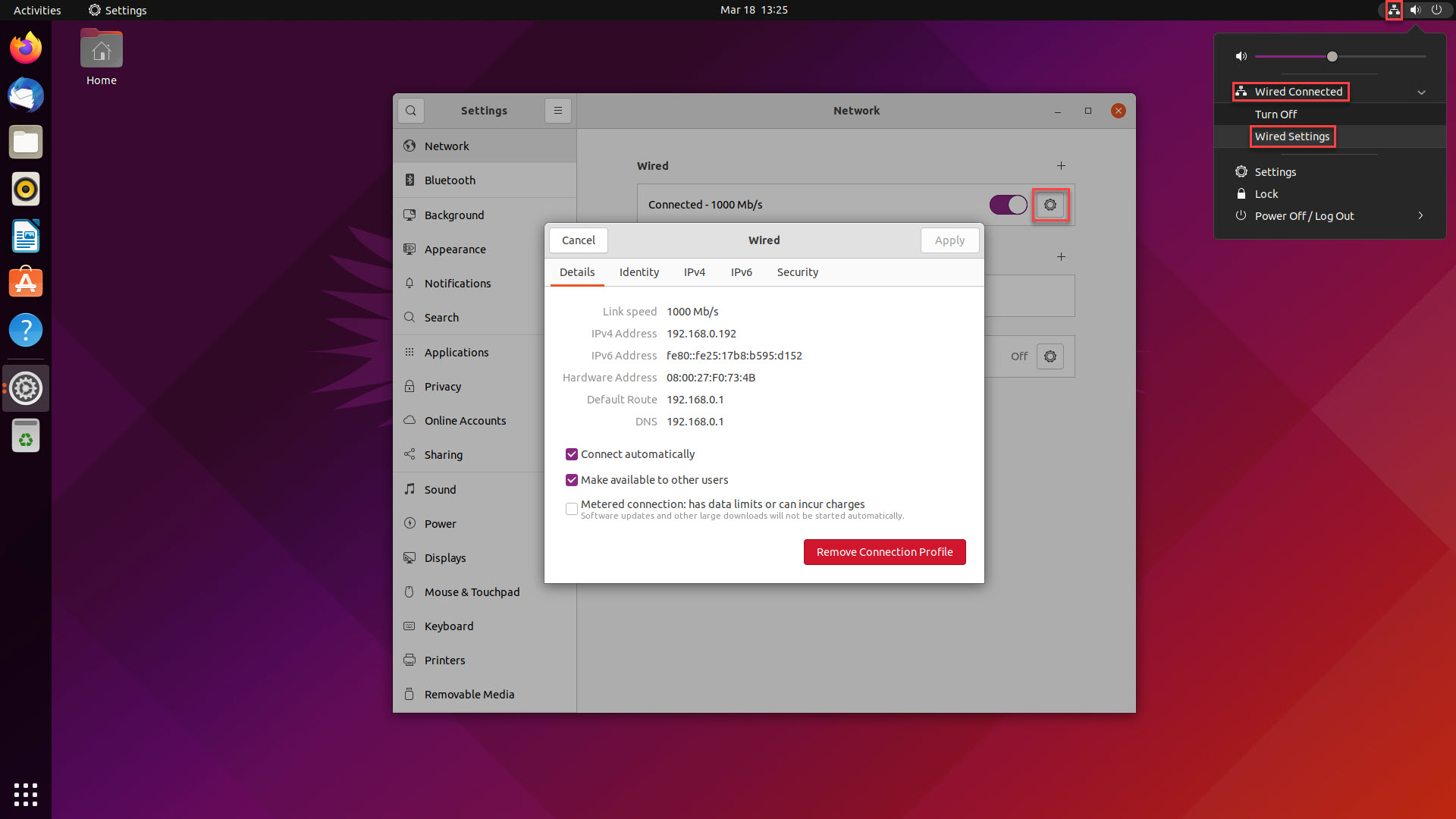
To connect to your Ubuntu machine via a VNC client, you'll need its IP address. This is the unique identifier that remote desktop clients use to establish a connection. To locate your IP address on Ubuntu, follow these simple steps:
- Click on the network icon at the top right of your screen to access the network settings.
- Select the network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) that you want to use for remote desktop access.
- In the Network Settings window, click on the cogwheel next to the active network connection.
- Scroll down to find your machine’s IPv4 Address. This is your Ubuntu machine’s IP address, which you’ll need to enter into your VNC client.
Once you've noted down the IP address, you’re ready to proceed to the next step—installing and configuring your VNC client for remote access.
Step 3: How to install a VNC client
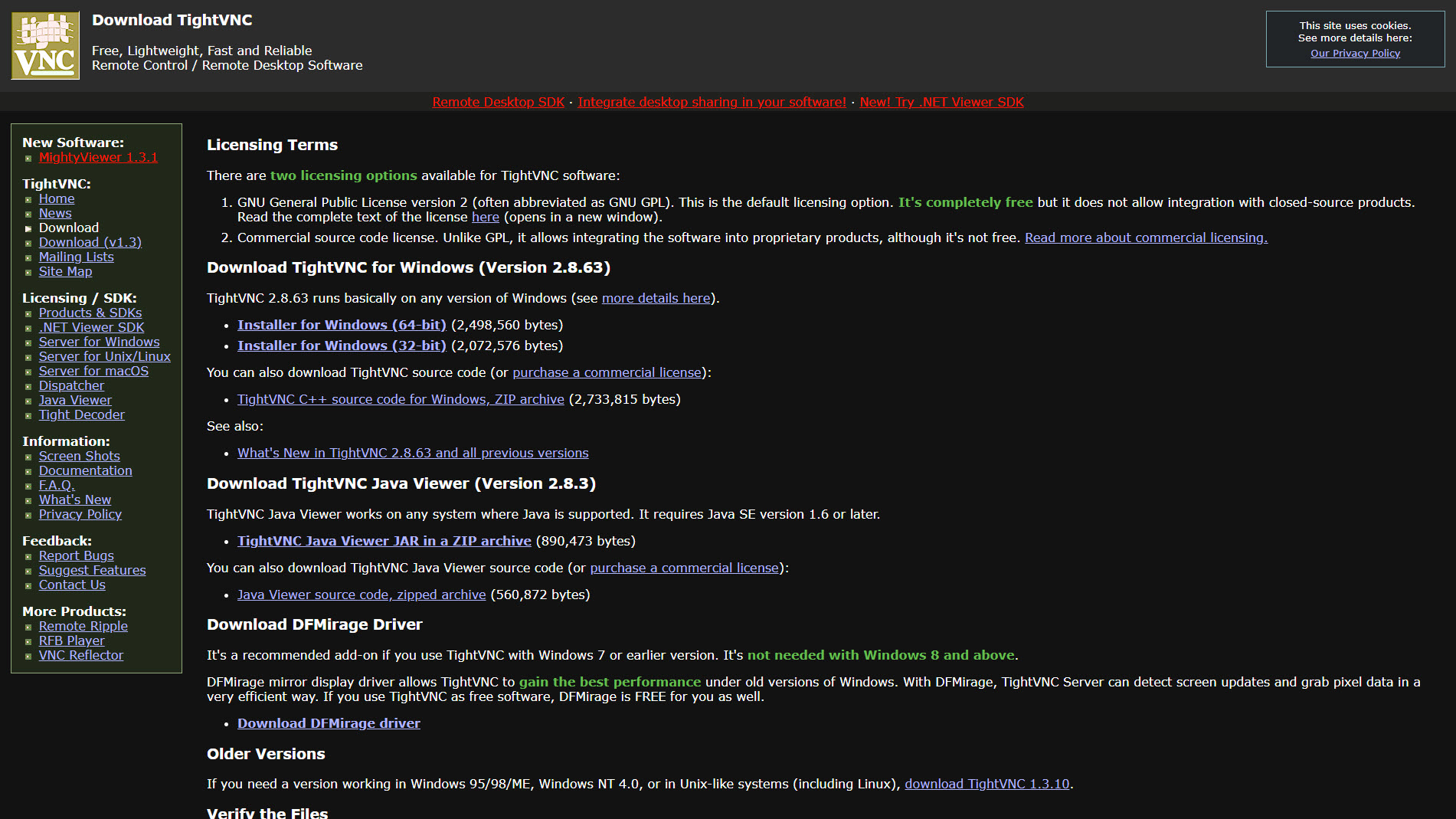
On the second device you want to use to connect to your Ubuntu machine, you will need a VNC client. If you’re connecting from Windows, there are free, open-source clients such as the aforementioned TightVNC, TigerVNC, and UltraVNC.
Download and install your choice of VNC client app. The installation process will vary, but VNC clients are typically simple, lightweight programs that require very little extra setup.
In our example, we’ll be using TightVNC. Download the TightVNC software, run through the installer, and you’re ready to go.
Step 4: How to remote desktop into Ubuntu
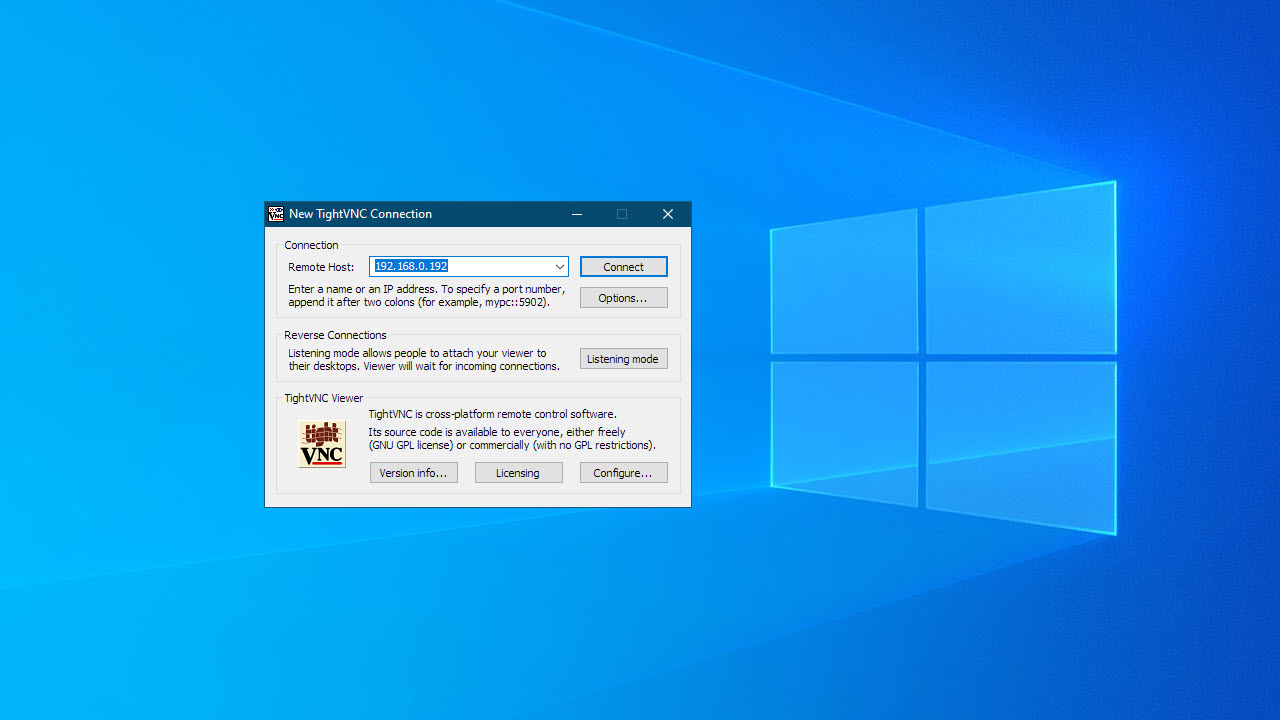
- Click on your VNC client app (sometimes called the viewer)
- Enter the IP address you made a note of earlier
- Click 'Connect'
- Depending on how you configured access earlier, you may need to enter a password next
- You should now have remote access to your Ubuntu computer
Optional step 5 for Windows users: How to use RDP
If you predominantly work with Microsoft Windows, you may be more comfortable using RDP to connect to your Ubuntu computer than VNC.
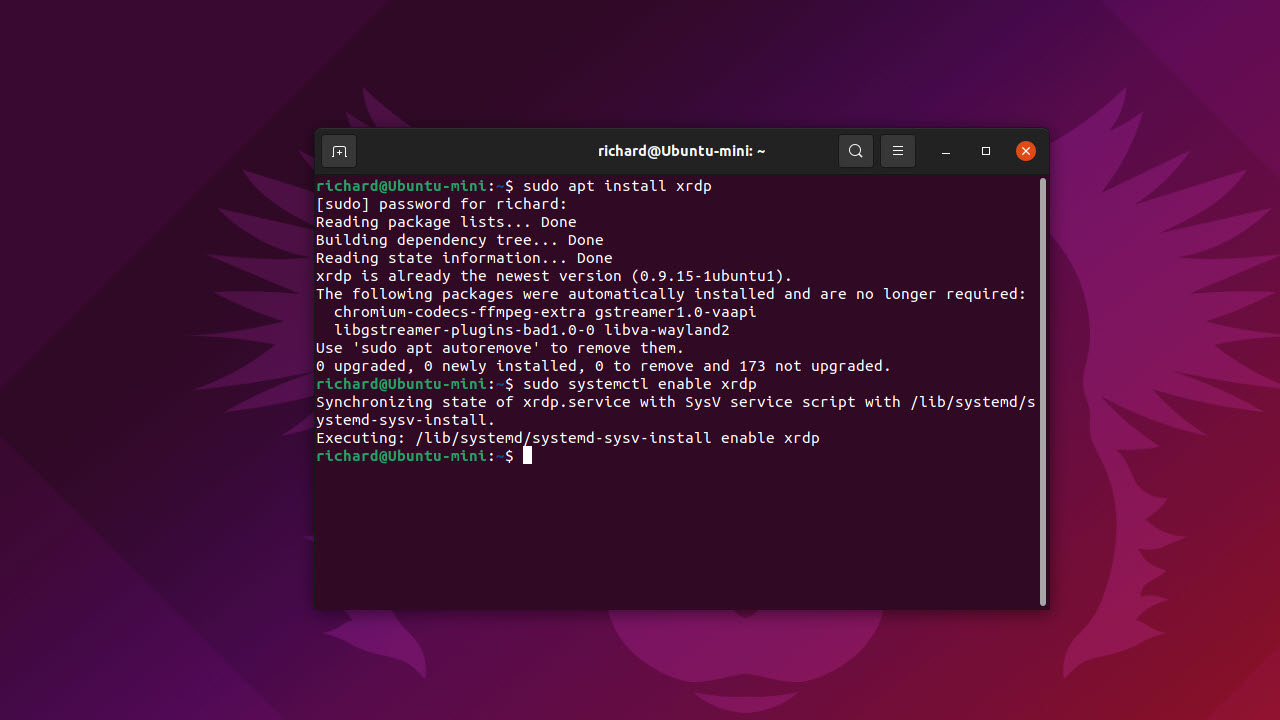
RDP is the protocol used by Microsoft Remote Desktop. It isn’t enabled by default on Ubuntu, but it’s easy to get it up and running by installing xRDP on your Ubuntu computer.
- To start, bring up the terminal (command line) on your Ubuntu computer by pressing Ctrl + Shift + T
- Enter the command ‘sudo apt install xrdp’, without the quotes, and press enter: you’ll need to enter your administrator password, and this command will download and install xRDP
- Now, enter the command ‘sudo systemctl enable xrdp’, without the quotes, and press enter: this will enable the xRDP listening service
Your Ubuntu computer is now able to accept RDP connections. You can use the software that’s built into all modern versions of Windows called Remote Desktop Connection, or download Remote Desktop clients for Android and iOS from their respective storefronts.
We’ve put together a guide on how to use Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection if you need guidance on using an RDP client.
Things to consider when using Ubuntu remote desktop
While the steps outlined above provide a straightforward way to remotely access your Ubuntu desktop, there are alternatives depending on your needs. If you only need command-line access, you can bypass the graphical interface entirely and use Secure Shell (SSH). SSH provides a secure, efficient way to manage your system remotely without the overhead of a full desktop environment.
RELATED RESOURCE

Discover why development and security teams need to adopt a responsible approach to AI
In addition to VNC and RDP, there are several other remote desktop solutions that offer seamless Ubuntu support. TeamViewer, for instance, is a widely-used commercial tool that allows you to access your Ubuntu machine remotely without extensive configuration. It’s a great choice if you need a quick and reliable option for remote support or access.
Chrome Remote Desktop is another possibility, especially for users already familiar with Google’s ecosystem. While it functions well as a VNC client on Ubuntu, setting it up for external device access can be a bit more involved compared to other solutions. Nonetheless, it’s a viable option for users comfortable with Google’s platform.
Further reading on remote desktops
If you’d like to dive deeper into remote desktop technologies, we offer a range of articles to help you explore different protocols and platforms. Learn more about key options like RDP, XRDP or VNC, and discover what TeamViewer has to offer. Additionally, if you're using Microsoft products, you might find our guide on Microsoft Remote Desktop particularly useful.
For those working with macOS, we also provide step-by-step instructions on setting up a remote desktop on a Mac, configuring Chrome Remote Desktop, and how to remote desktop from Mac to Windows.
Troubleshooting common remote desktop issues on Ubuntu
Even with a robust setup, users may occasionally run into issues when trying to remote desktop into Ubuntu. Here are a few common problems and how to resolve them:
- Connection timeout: Ensure that both machines are on the same network (if applicable) and that the IP address you’re using is correct. Double-check your firewall settings to ensure remote desktop ports (like 5900 for VNC or 3389 for RDP) are open.
- Authentication failures: If you’re unable to authenticate, revisit your password setup in the screen sharing or xRDP configuration. Also, verify that your username is correctly entered.
- Screen resolution issues: Some users experience screen resolution problems when connecting via VNC. Adjust the resolution settings on both your client and server to find an optimal display size.
- Lag or slow performance: Network latency can cause lag in remote desktop sessions. Try connecting over a wired Ethernet connection or ensure your Wi-Fi is stable with minimal interference.
- Security concerns: Remote desktop access can expose your system to potential threats. Ensure that your connection is secure by using encrypted protocols and strong passwords, and consider using VPN or SSH tunnels for an added layer of security.
Richard brings more than 20 years of computer science, full-stack development and business operations experience to ITPro. A graduate in Computer Science and former IT support manager at Samsung, Richard has taught courses in Java, PHP and Perl, and developed software for both private businesses and state organisations. A prolific author in B2B and B2C tech, Richard has written material for Samsung, TechRadar Pro, and now ITPro.